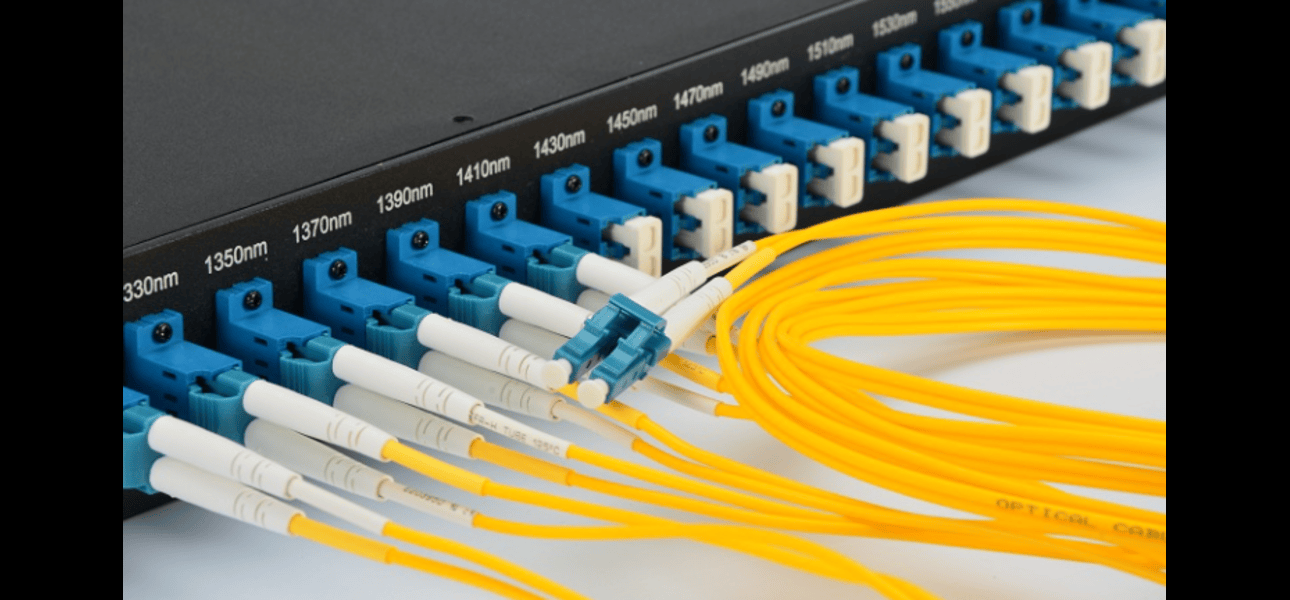
As the demand for high-speed data transmission continues to grow in today’s digital age, data centers have become the backbone of the internet, cloud computing, and digital services. One of the key components that make high-performance data centers possible is fiber optic cables. These cables are known for their ability to provide high bandwidth, low latency, and high reliability, making them the preferred choice for data transmission in data centers. In this blog post, we will explore the common types of fiber optic cables used in data centers and their specific applications, helping you understand how to choose the right one for your needs.
Overview of Fiber Optic Technology
Basics of Fiber Optic Cables: Fiber optic cables are designed to transmit data as light signals through strands of glass or plastic fibers. The core of the fiber optic cable, which is the central part, is where the light signals travel. Surrounding the core is the cladding, a layer of material that reflects light back into the core to minimize signal loss. The entire structure is protected by a buffer coating that shields the fibers from moisture, physical damage, and other environmental factors.
Advantages of Fiber Optics: Compared to traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables offer several advantages. They provide higher bandwidth, allowing for faster data transmission over longer distances. Fiber optics are also immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt data transmission in copper cables. Additionally, fiber optic cables are lighter, thinner, and more durable, making them ideal for use in data centers where space and reliability are crucial.
Common Types of Fiber Optic Cables Used in Data Centers
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF)
- Description: Single-mode fiber (SMF) is designed to carry light signals directly down the fiber with minimal dispersion. This type of fiber uses a small core, typically around 9 microns in diameter, which allows only one mode of light to pass through.
- Applications: SMF is ideal for long-distance communication and high-bandwidth applications, such as backbone connections in data centers, metro area networks (MANs), and long-haul telecommunications.
- Advantages and Limitations: The main advantages of SMF include its ability to transmit signals over longer distances with less signal loss and support higher bandwidths compared to multi-mode fibers. However, it is generally more expensive and requires more precise alignment of connectors, making installation and maintenance more challenging.

Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF)
- Description: Multi-mode fiber (MMF) has a larger core diameter, typically ranging from 50 to 62.5 microns, allowing multiple modes of light to propagate through the fiber. This makes it suitable for short-distance communication where multiple signals can be transmitted simultaneously.
- Types of MMF: MMF cables are categorized into different types based on their performance characteristics: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5. These categories differ in terms of core size, bandwidth, and distance capabilities. OM1 and OM2 are typically used for lower bandwidth and short distances, while OM3, OM4, and OM5 are designed for higher bandwidths and longer distances up to 550 meters.
- Applications: MMF is commonly used in data centers for short-distance connections, such as within a single building or between buildings on the same campus. It is also widely used in local area networks (LANs) and storage area networks (SANs).
- Advantages and Limitations: MMF is more cost-effective for short-distance applications and easier to splice than SMF. However, it has a shorter transmission distance due to higher attenuation and dispersion, which limits its use in long-distance applications.

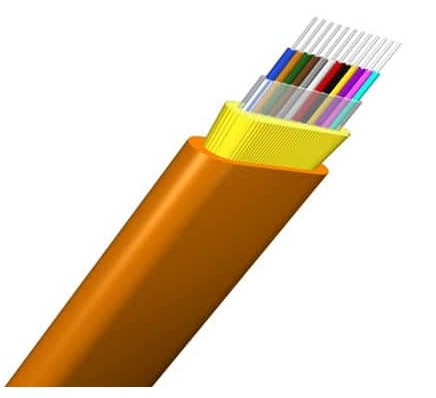
Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables
- Description: Ribbon fiber optic cables consist of multiple fibers laid side by side in a flat, ribbon-like structure. This design allows for high fiber density and efficient mass fusion splicing, which can save time and reduce labor costs during installation.
- Applications: Ribbon cables are particularly useful in high-density environments, such as data centers and telecom networks, where space is at a premium and a large number of connections need to be managed.
- Advantages and Limitations: The advantages of ribbon cables include their high density, which allows for a large number of fibers in a small space, and the ability to splice multiple fibers simultaneously. However, they can be more difficult to handle due to their rigidity, and the cost can be higher compared to traditional fiber cables.
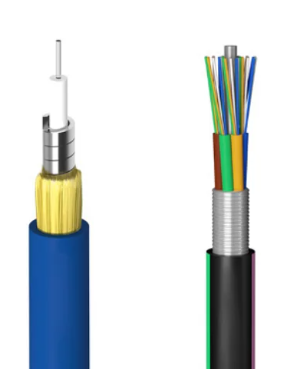
Armored Fiber Optic Cables
- Description: Armored fiber optic cables are designed with an additional layer of protection around the fiber core to prevent physical damage. This armor can be made from various materials, such as steel or aluminum, providing enhanced durability in harsh environments.
- Applications: These cables are ideal for use in environments where the cable is exposed to physical stress or potential damage, such as in data centers with high physical security needs, outdoor installations, or industrial settings.
- Advantages and Limitations: Armored cables offer robust protection against mechanical damage and rodent attacks, making them suitable for tough environments. However, they are less flexible, which can make installation more challenging, and they are generally more expensive than non-armored cables.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Fiber Optic Cables for Data Centers
- Distance and Bandwidth Requirements: The choice between single-mode and multi-mode fibers often depends on the required transmission distance and bandwidth. For long-distance and high-bandwidth needs, single-mode fibers are more appropriate. For shorter distances and lower bandwidth requirements, multi-mode fibers are a cost-effective choice.
- Environmental Considerations: Consider the environment where the cables will be installed. If the installation area is prone to physical damage, armored cables might be necessary. In high-density environments, ribbon cables could provide the needed space efficiency.
- Future-Proofing: It’s essential to consider future upgrades and expansions when selecting fiber optic cables. Opting for higher performance cables, like OM4 or OM5 multi-mode fibers, may provide more longevity and adaptability to future technologies.
- Cost: While fiber optic cables offer numerous advantages, they can vary significantly in cost. Single-mode fibers and armored cables tend to be more expensive than multi-mode and standard cables. Balancing performance requirements with budget constraints is crucial when making a selection.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of fiber optic cable for your data center is a critical decision that can impact performance, scalability, and cost. Single-mode fibers are ideal for long-distance and high-bandwidth applications, while multi-mode fibers are suitable for shorter distances and more cost-sensitive environments. Ribbon and armored cables offer unique advantages for high-density and high-security environments, respectively. By considering factors such as distance, bandwidth, environmental conditions, future-proofing, and cost, you can make an informed decision that meets your data center’s needs.